cvi42 plaque
cvi42 | Plaque
See More Than Stenosis. Quantify Risk. Personalize Care.
AI-enabled coronary plaque quantification directly from your CCTA.
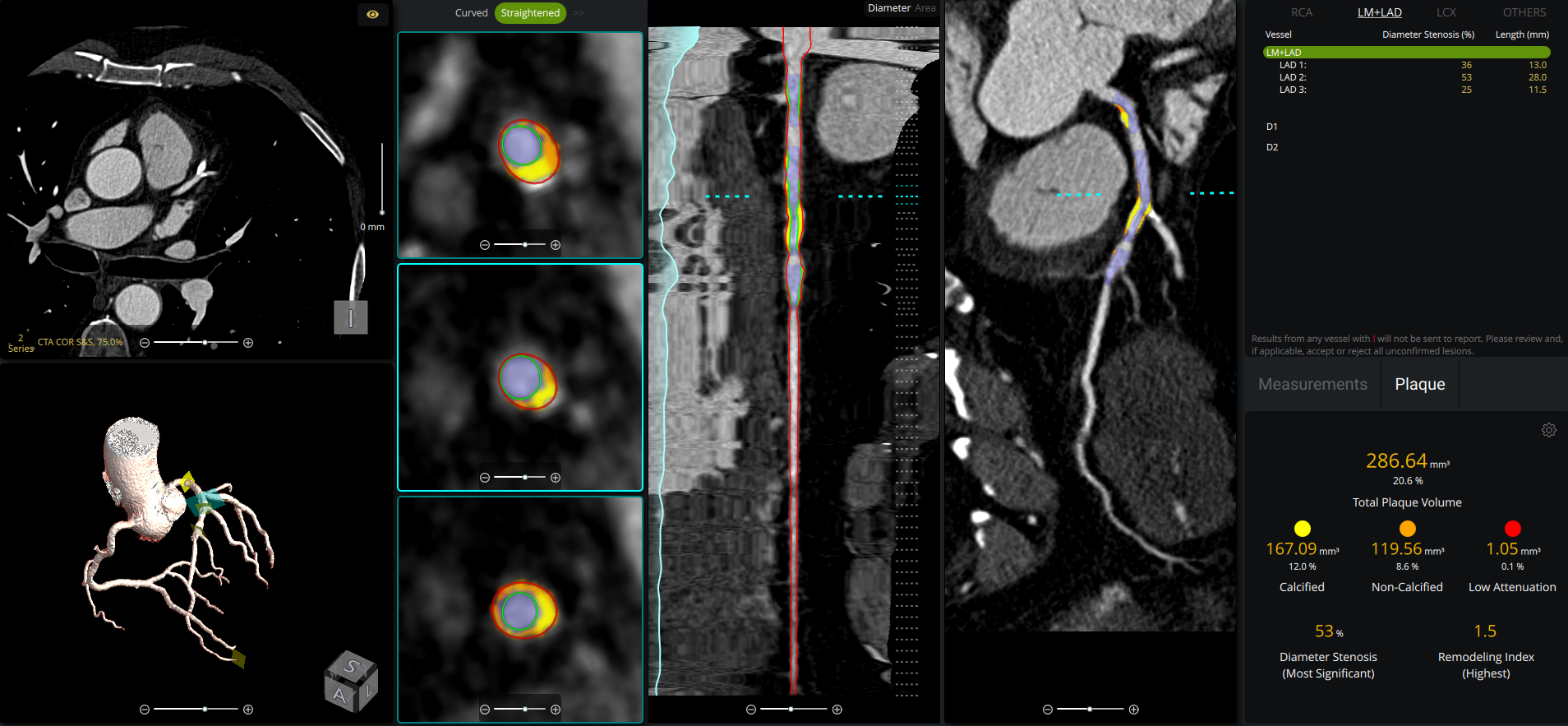
Why Choose cvi42 | Plaque?
Fast. Reproducible. Integrated.
cvi42 | Plaque empowers cardiac imaging teams with AI-enabled, on-premise quantification of atherosclerotic burden for clinical use. It delivers precise measurements of plaque volume, burden, composition, and distribution, all fully integrated into your CT workflow, without the need to send away to an outside reading service.
AI-Enabled Automation:
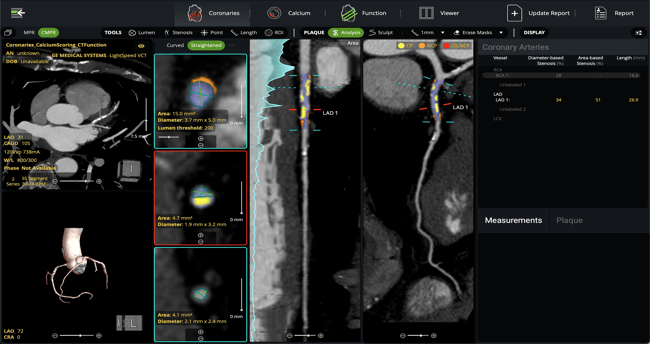
- Automated coronary lumen and wall segmentation ensures rapid, reproducible plaque quantification
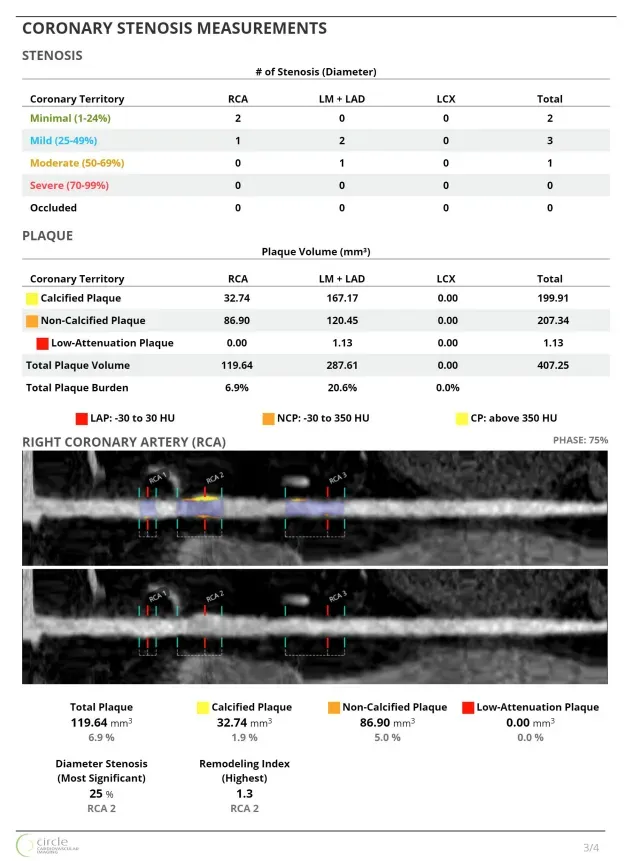
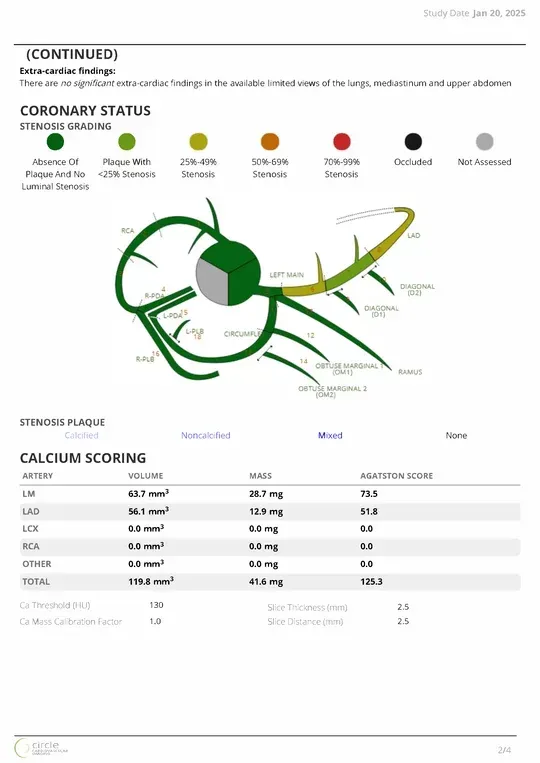
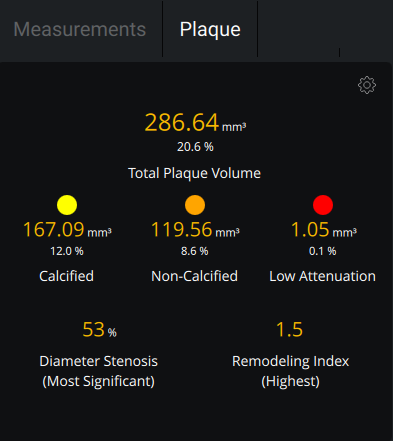
- Per-lesion and per-vessel analysis provides detailed assessment of calcified, non-calcified, and low attenuation plaque for precise risk stratification
- Remodeling index calculation identifies high-risk plaques beyond stenosis severity
Operational Efficiency:
- Decrease turnaround times for coronary plaque studies with in-house reading
- Directly access and retain reimbursement for plaque imaging services performed internally
- Reduce PHI privacy and security risks with no data leaving the hospital
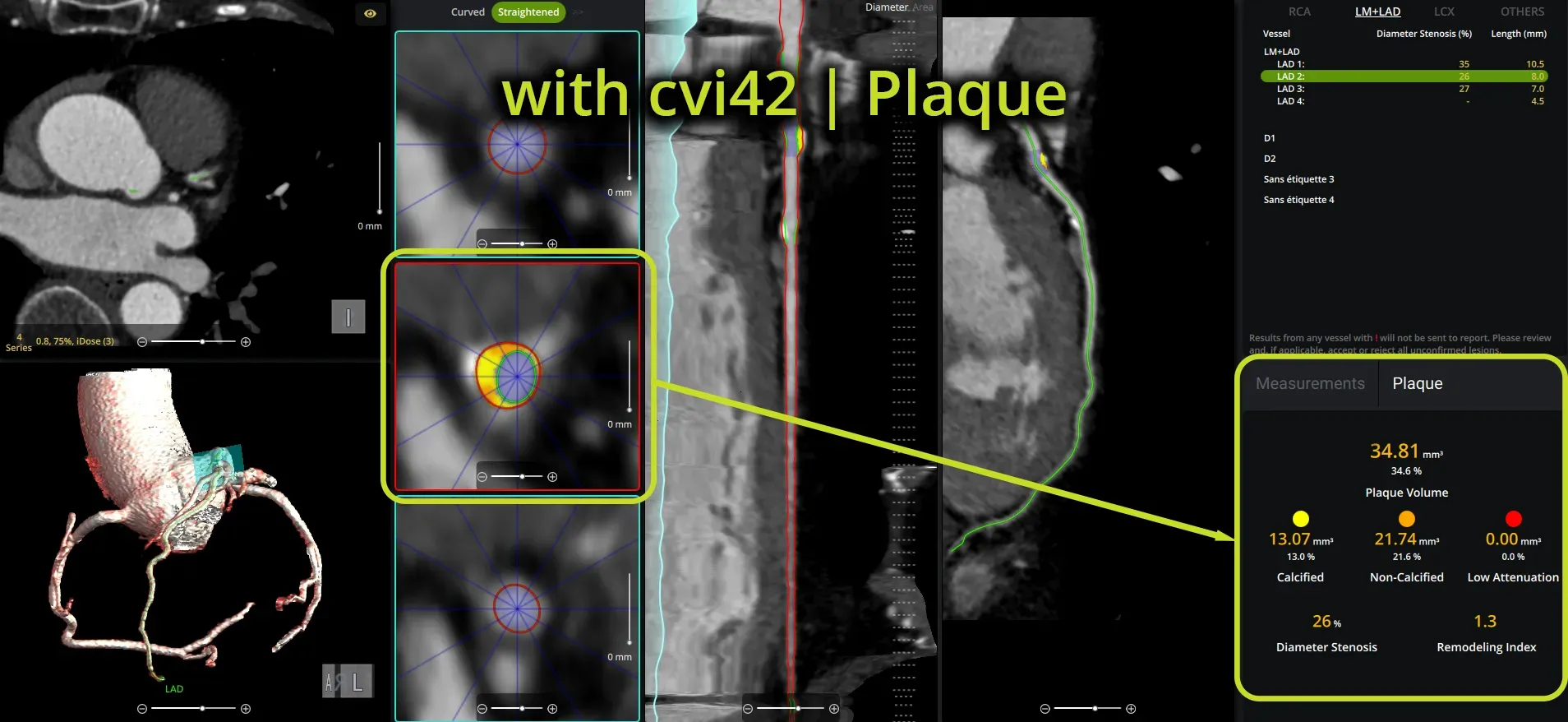
Smart, Actionable Reporting
- Generate vessel-level and total plaque summaries for fast and
- clear interpretation
- Visual, patient-friendly outputs improve communication and support shared decision-making
- Integrated CAD-RADS classification supports standardized reporting and facilitates communication across the care team
Full User Control:
- Manual controls allow adjustment of lumen, vessel wall, and lesion annotations as needed
- Lesion-level occlusion marking enhances detection of chronic total occlusions and supports revascularization planning
- Option of single- or dual-reference markers allows flexibility in grading stenosis
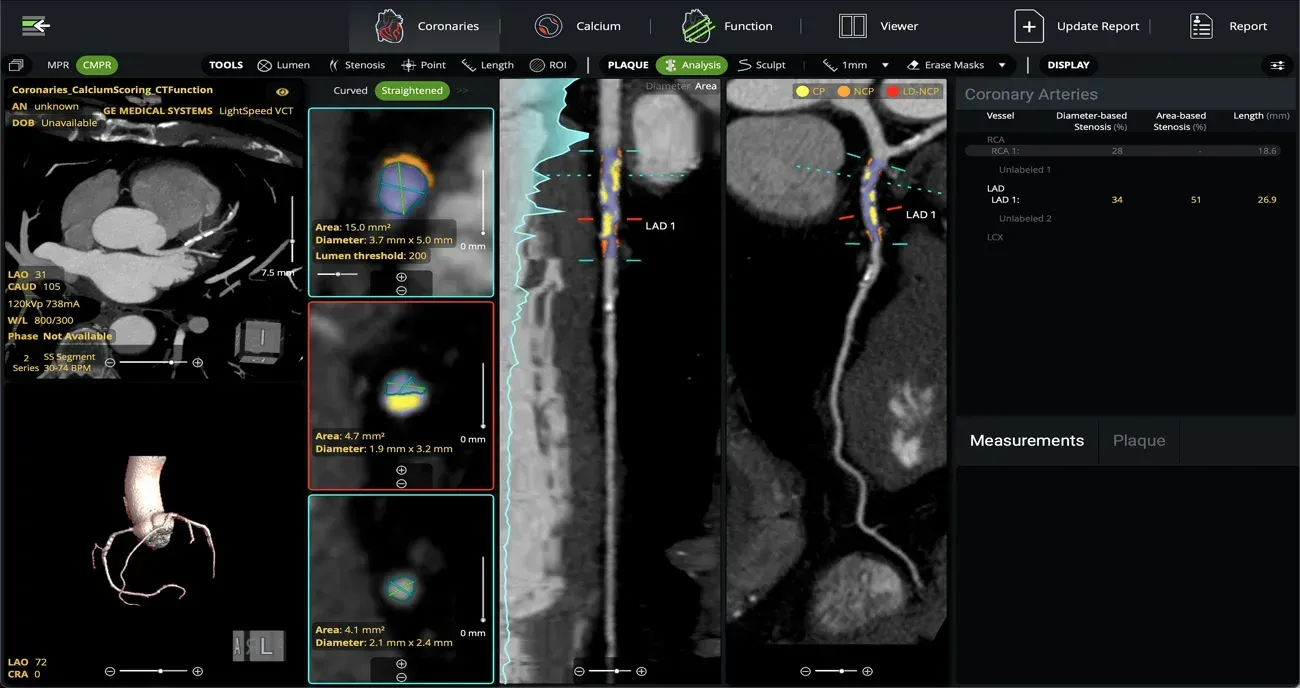
Why CT plaque quantification?
Traditional stenosis assessment doesn’t tell the whole story.
CT-derived plaque quantification provides a comprehensive, objective, and actionable assessment of coronary atherosclerosis by quantifying total, non-calcified, and high-risk plaque¹. This insight enhances diagnosis, improves risk stratification, and informs more personalized care.
Proven Predictive Value:
- Offers superior prognostic information compared to stenosis-based or traditional risk-factor assessments8
- Identifies High-Risk features such as low-attenuation plaques (<60HU) and remodeling index whichin dependently predict adverse cardiac events(2,3,4)
Reliable and Reproducible:
Demonstrates strong concordance with invasive imaging (IVUS), in assessing plaque volume and composition(5)
AI-enhanced volumetric analysis ensures fast, consistent, and reproducible results.
Personalized Treatment & Longitudinal Monitoring:
- Enables tracking of treatment-induced changes, such as statin-induced plaque regression(6,7)
- Detects vulnerable plaque features (e.g., low-attenuation <30 HU, positive remodeling) linked to elevated event risk(10)
- Engage patients with visual evidence: Support patient adherence with intuitive, visual explanations of disease progression
Better Cardiovascular Outcomes Through Prevention:
- CCTA offers incremental predictive value beyond coronary calcification and clinical scores, by assessing non-calcified and low-attenuation plaque burden.(9)
- CCTA has been shown to modestly encourage healthier lifestyle choices, greater acceptance of preventive treatments, and positive changes in risk factors.(11)
References
1. Mézquita AJV, Biavati F, Falk V, et al. Clinical quantitative coronary artery stenosis and coronary atherosclerosis imaging: a Consensus Statement from the Quantitative Cardiovascular Imaging Study Group. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023;20(10):696-714. doi:10.1038/s41569-023-00880-4
2. Feuchtner G, Kerber J, Burghard P, et al. The high-risk criteria low-attenuation plaque <60 HU and the napkinring sign are the most powerful predictors of MACE: a long-term follow-up study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017;18(7):772-779. doi:10.1093/ehjci/jew167
3. Deseive S, Straub R, Kupke M, et al. Quantification of coronary low-attenuation plaque volume for long-term prediction of cardiac events and reclassification of patients. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2018;12(2):118-124. doi:10.1016/j.jcct.2018.01.002
4. Williams MC, Moss AJ, Dweck M, et al. Coronary Artery Plaque Characteristics Associated With Adverse Outcomes in the SCOTHEART Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(3):291-301. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.066
5. Shaw LJ, Blankstein R, Bax JJ, et al. Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography / North American Society of Cardiovascular Imaging - Expert Consensus Document on Coronary CT Imaging of Atherosclerotic Plaque. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2021;15(2):93-109. doi:10.1016/j.jcct.2020.11.002
6. Zeb I, Li D, Nasir K, et al. Effect of statin treatment on coronary plaque progression - a serial coronary CT angiography study. Atherosclerosis. 2013;231(2):198-204. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.08.019
7. Lee SE, Chang HJ, Sung JM, et al. Effects of Statins on Coronary Atherosclerotic Plaques: The PARADIGM Study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;11(10):1475-1484. doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.04.015
8. Hadamitzky M, Achenbach S, Al-Mallah M, et al. Optimized prognostic score for coronary computed tomographic angiography: results from the CONFIRM registry (Coronary CT Angiography Evaluation For Clinical Outcomes: An International Multicenter Registry). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(5):468-476. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.04.064
9. Williams MC, Kwiecinski J, Doris M, et al. Low-Attenuation Noncalcified Plaque on Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography Predicts Myocardial Infarction: Results From the Multicenter SCOT-HEART Trial (Scottish Computed Tomography of the HEART). Circulation. 2020;141(18):1452-1462. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044720
10. Motoyama S, Sarai M, Harigaya H, et al. Computed tomographic angiography characteristics of atherosclerotic plaques subsequently resulting in acute coronary syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(1):49-57. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.068
Brief Summary: Indications, contraindications warnings and precautions can be found in the product labelling.
Disclaimer: Not all modules or features are available in every region. Contact your local Circle representative for all regional availability.
CAUTION: Federal law (USA) restricts these devices for sale by, or on the order of a physician. The system is intended for use only by trained Healthcare Professionals.
Why Circle?
Our automated platform increases productivity while streamlining reporting. Reclaim lost time by optimizing decision-making with our cutting-edge AI platform and our unique expertise.

Our Technology Enables Informed Decisions for Fast and Accurate Diagnoses

Automated Workflows Increase Time for Patient Care

Unmatched User Experience & Support You Can Count On